A recent study explored the effectiveness of Digital Drug Assignment (DDA)
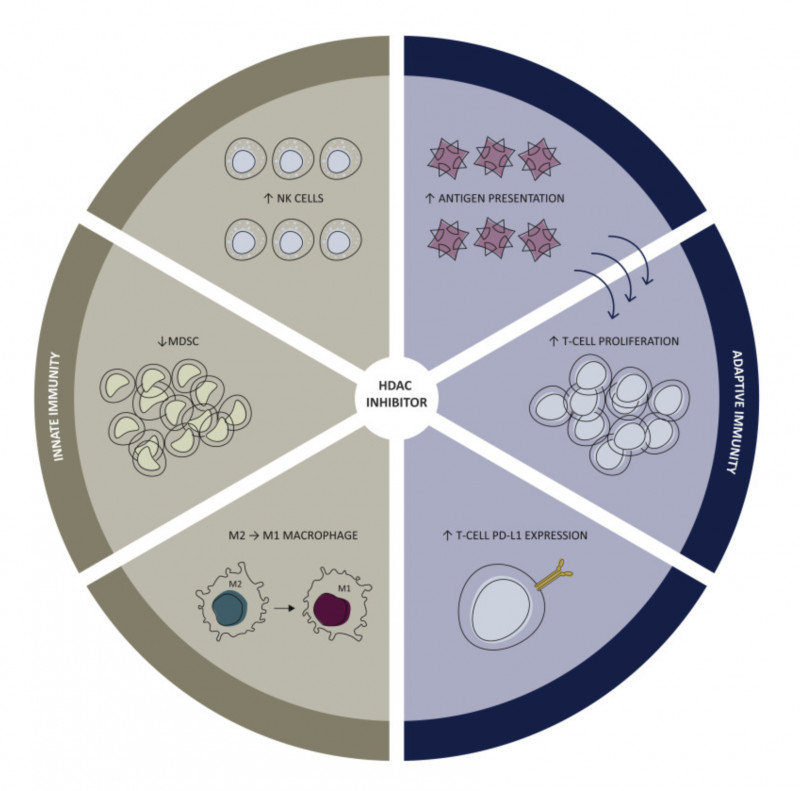
A recent study explored the effectiveness of Digital Drug Assignment (DDA), an innovative computational method aimed at optimizing treatment strategies for pediatric cancer patients. DDA's goal is to prioritize treatment options based on a vast array of genetic information, assisting doctors in selecting the most effective medication for their patients.
The study involved 103 high-risk pediatric cancer patients between 2017 and 2020, with samples from 100 patients eligible for further analysis. Through various genetic tests, mutations in cancer cells were identified, and the DDA algorithm was used to formulate a treatment recommendation. Subsequently, a group of experts evaluated the results and provided treatment advice.
The findings revealed that in 56 of the 72 cases (78%) where the DDA method identified actionable treatment options, the recommended therapies were backed by higher levels of scientific evidence compared to those not recommended. This indicates that the DDA method could significantly improve the quality of treatment for children suffering from cancer by offering more accurate and targeted treatment options.
In summary, the study demonstrates that DDA is a promising tool in pediatric oncology, aiding in the interpretation of complex genetic information and thus facilitating the development of more precise, personalized treatment plans.